What’s the Difference Between a Franchise and Corporation? Explained
A franchise is a business model where individuals operate under a brand’s name, while a corporation is a single

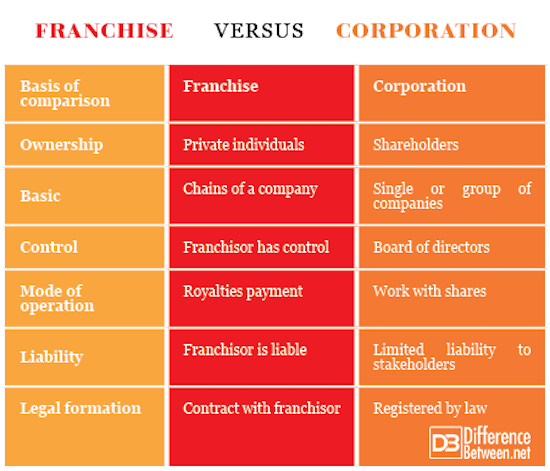
A franchise is a business model where individuals operate under a brand’s name, while a corporation is a single legal entity. Franchises are owned by franchisees, and corporations are owned by shareholders.
Franchises allow entrepreneurs to run their own businesses using an established brand and support system. This includes access to the brand’s products, services, and operating procedures. Corporations, on the other hand, are structured as a single legal entity that can own multiple businesses and is managed by a board of directors.
Both models offer unique advantages and challenges. Franchises provide a proven business model with support, while corporations offer centralized control and potential for large-scale growth. Understanding these differences helps in making informed business decisions.
Franchise Basics
Understanding Franchise Basics is essential for grasping the key differences between a franchise and a corporation. A franchise allows individuals to operate a business under an established brand. Let’s dive into the essentials of what makes a franchise unique.
Definition Of A Franchise
A franchise is a business model where the owner, called the franchisor, grants licenses to third parties, called franchisees. This license allows them to operate their own businesses using the franchisor’s brand, systems, and support.
Franchises operate under a legal agreement that outlines the terms and conditions. The franchisee pays an initial fee and ongoing royalties to the franchisor. In return, they receive training, support, and the right to use the brand name.
Types Of Franchises
There are several types of franchises, each with its own characteristics. Here are the most common types:
- Product Distribution Franchise: The franchisee sells the franchisor’s products. Examples include car dealerships and soft drink distributors.
- Business Format Franchise: The franchisee adopts the franchisor’s entire business model. This includes marketing strategies, operational guidelines, and branding. Fast-food chains like McDonald’s are examples.
- Manufacturing Franchise: The franchisee manufactures and sells products using the franchisor’s brand and formula. Soft drink bottling companies are a common example.
| Type of Franchise | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Product Distribution Franchise | Franchisee sells the franchisor’s products. | Car dealerships, Soft drink distributors |
| Business Format Franchise | Franchisee adopts the franchisor’s entire business model. | Fast-food chains like McDonald’s |
| Manufacturing Franchise | Franchisee manufactures and sells products using the franchisor’s brand. | Soft drink bottling companies |
Understanding these types helps in making informed decisions about entering the franchise business. Each type offers unique benefits and challenges.
Corporation Essentials
Understanding the basics of a corporation is crucial. It helps differentiate it from other business structures. A corporation is a legal entity that is separate from its owners. This separation provides unique advantages and responsibilities.
Definition Of A Corporation
A corporation is a business entity recognized by law as separate from its owners. This means the corporation itself can own assets, incur liabilities, and enter into contracts. Owners of a corporation are called shareholders. They invest money in the business and receive shares of stock in return.
Corporations offer limited liability protection. This means shareholders are not personally liable for the corporation’s debts. This protection is a key feature that attracts many business owners. Corporations also have perpetual existence, meaning they continue to exist even if the owners change or pass away.
Types Of Corporations
There are various types of corporations, each with unique features. Here are some common types:
- C Corporation (C Corp): The most common type of corporation. It is taxed separately from its owners.
- S Corporation (S Corp): Offers tax benefits by passing income directly to shareholders, avoiding double taxation.
- Nonprofit Corporation: Operates for charitable, educational, or similar purposes. Profits are not distributed to shareholders.
- Professional Corporation (PC): Used by licensed professionals like doctors and lawyers. Provides limited liability protection.
- Benefit Corporation (B Corp): Focuses on providing a public benefit while still making a profit.
| Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
| C Corporation (C Corp) | Taxed separately from owners, unlimited shareholders, can raise capital easily. |
| S Corporation (S Corp) | Passes income to shareholders to avoid double taxation, limited to 100 shareholders. |
| Nonprofit Corporation | Operates for public benefit, profits not distributed to shareholders. |
| Professional Corporation (PC) | Used by licensed professionals, limited liability protection. |
| Benefit Corporation (B Corp) | Focuses on public benefit, can still make a profit. |
Ownership And Control
Understanding the ownership and control differences between a franchise and a corporation is essential. These differences affect how each business operates and makes decisions. In this section, we will explore the nuances of franchise ownership and corporate ownership.
Franchise Ownership
In a franchise, the franchisee buys the right to use a brand’s name and system. The franchisor provides guidelines and support. The franchisee follows these guidelines to maintain brand consistency.
Franchisees own their individual units. They invest their money and manage daily operations. They must adhere to the franchisor’s rules and standards. Here are some key points about franchise ownership:
- Franchisees have significant control over their units.
- They benefit from established brand recognition.
- Franchisees pay fees and royalties to the franchisor.
- They receive training and support from the franchisor.
Corporate Ownership
In a corporation, the company is owned by shareholders. These shareholders invest money and own shares of the company. A board of directors manages the corporation’s affairs.
Corporate ownership involves centralized control. The board makes major decisions and sets policies. Here are some key points about corporate ownership:
- Shareholders have limited involvement in daily operations.
- The board of directors oversees the company.
- Profits are shared among shareholders as dividends.
- Corporations can raise capital by issuing shares.
Understanding these differences helps in making informed business decisions. Both models offer unique opportunities and challenges.
Financial Structure
The financial structure of a business can significantly impact its growth and management. Understanding the differences between a franchise and a corporation is crucial for potential investors and entrepreneurs. This section delves into the distinct financial characteristics of both models.
Franchise Investment
Franchises typically involve a one-time initial fee and ongoing royalties. The initial fee covers the right to use the brand and systems.
- Initial Fee: Ranges from $10,000 to $100,000
- Ongoing Royalties: Usually 4% to 12% of gross sales
- Marketing Fees: Often 1% to 4% of gross sales
The franchisee is responsible for funding the location, staff, and daily operations. This includes costs like rent, utilities, and supplies. The franchise model allows for lower risk due to established brand recognition and support.
Corporate Funding
Corporations often raise funds through equity and debt. The equity method involves selling shares of the company.
- Equity: Selling shares to investors
- Debt: Taking loans or issuing bonds
Corporations may also reinvest their profits back into the business. This allows for greater control over the company’s direction and growth. The corporate model typically involves higher risk but offers unlimited growth potential.
The financial structure of a corporation is generally more complex. It includes elements like dividends, retained earnings, and stock options.
| Aspect | Franchise | Corporation |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | $10,000 – $100,000 | Varies (Equity, Debt) |
| Ongoing Fees | Royalties, Marketing Fees | None |
| Funding Sources | Franchisee | Equity, Debt |
| Risk Level | Lower | Higher |
| Growth Potential | Limited | Unlimited |
In summary, understanding the financial structure can guide your decision in choosing between a franchise and a corporation.
Legal Considerations
Understanding the legal considerations is crucial when comparing franchises and corporations. Knowing the differences can help in making informed business decisions. Below, we delve into two key areas: Franchise Agreements and Corporate Regulations.
Franchise Agreements
A franchise agreement is a legal document between the franchisor and franchisee. It outlines the rights and responsibilities of both parties. This agreement covers aspects like:
- Use of brand name
- Operational guidelines
- Franchise fees
- Territorial rights
- Training and support
Franchise agreements are often detailed. They ensure consistency across different franchise locations. Each agreement is unique, tailored to the specific franchise.
Corporate Regulations
A corporation operates under corporate laws. These laws vary by country and state. Corporations must follow strict regulations, such as:
- Filing annual reports
- Paying corporate taxes
- Holding regular board meetings
- Issuing stock
- Maintaining corporate records
Corporate regulations are designed to ensure accountability and transparency. They protect shareholders and the public. Corporations are considered separate legal entities, which means they can own property, sue, and be sued.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between A Franchise And A Corporation?
A franchise is a business model where individuals operate under a brand’s name. A corporation is a company owned by shareholders.
What Is The Difference Between A Franchise And A Corporate Chain?
A franchise is owned by individual operators, while a corporate chain is owned and managed by a central company. Franchisees pay fees and royalties to the franchisor. Corporate chains maintain complete control over all locations.
Is Mcdonald’s A Franchise Or Corporation?
McDonald’s operates as both a corporation and a franchise. The company owns some locations, while franchisees run others. This hybrid model allows rapid expansion and local management.
Is Corporate Better Than Franchise?
Choosing between corporate and franchise depends on your goals. Corporates offer more control, while franchises provide established systems and brand recognition.
Conclusion
Choosing between a franchise and a corporation depends on your business goals. Franchises offer a proven model and support. Corporations provide full control but come with higher risks. Understanding these differences helps make informed decisions. Evaluate your objectives and resources to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial journey.















